Biogeochemical cycles are essential processes that transfer elements and compounds between living organisms and the environment. These cycles play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of nutrients and energy within ecosystems. There are several biogeochemical cycles, including the carbon cycle, nitrogen cycle, and water cycle.
Each cycle involves a series of interconnected pathways through which elements are continuously recycled and reused. Understanding these cycles is vital for ecological sustainability and the health of our planet.
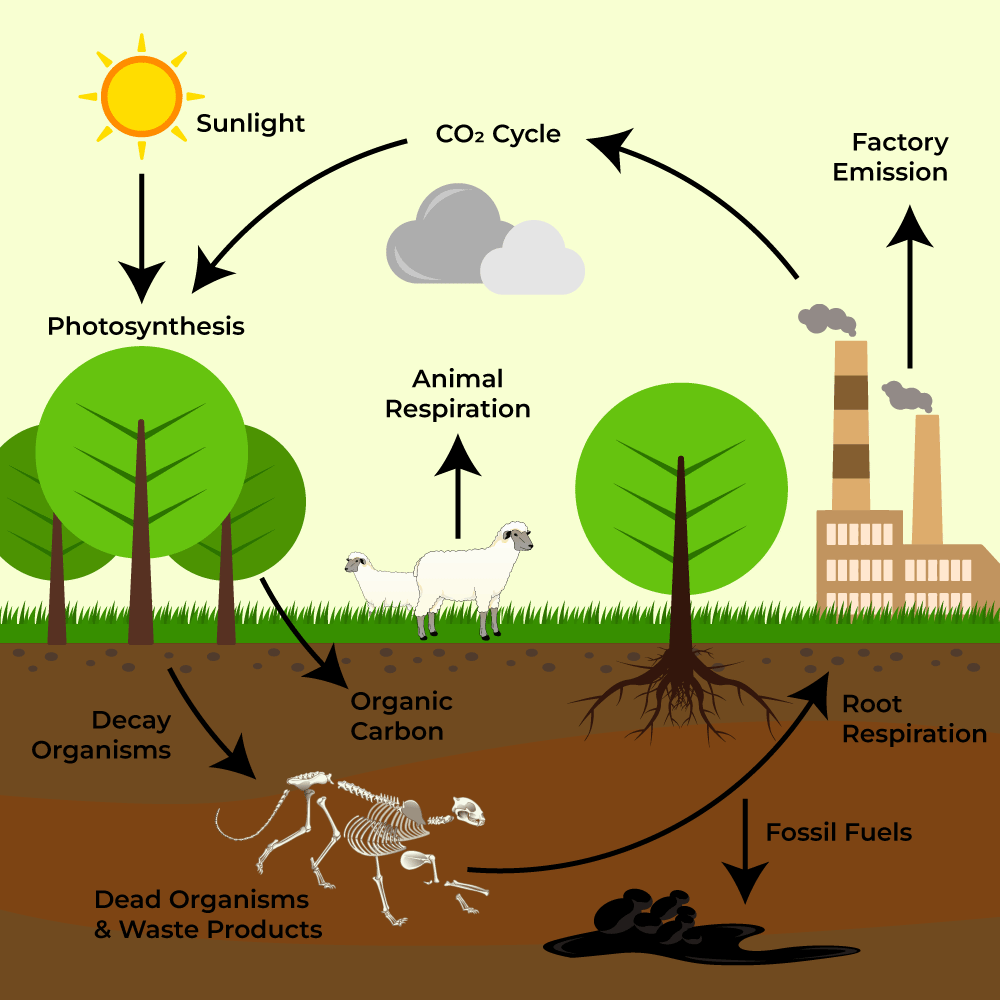
Biogeochemical Cycles Easy Drawing

The carbon cycle is one of the most well-known biogeochemical cycles. It involves the movement of carbon between the atmosphere, oceans, soil, and living organisms. Plants take in carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through photosynthesis, which is then passed on to animals when they consume plants. When organisms die, carbon is returned to the soil and eventually released back into the atmosphere through decomposition or combustion.
Another important cycle is the nitrogen cycle, which is essential for the growth of plants and the production of proteins. Nitrogen gas makes up a large portion of the Earth’s atmosphere, but most plants cannot use it in this form. Bacteria play a crucial role in converting nitrogen gas into a form that plants can absorb, known as nitrogen fixation. This process allows nitrogen to be cycled through the soil, plants, animals, and back into the atmosphere.
The water cycle, also known as the hydrological cycle, is responsible for the movement of water between the atmosphere, land, and oceans. Evaporation from bodies of water, transpiration from plants, and precipitation all play a role in this cycle. Water is essential for all life on Earth, and the water cycle ensures that this precious resource is continuously recycled and distributed throughout the planet.
Overall, biogeochemical cycles are complex yet essential processes that sustain life on Earth. By understanding and respecting these cycles, we can work towards preserving the health of our planet and ensuring a sustainable future for all living organisms.
In conclusion, biogeochemical cycles are intricate systems that regulate the flow of elements and compounds throughout the environment. Through processes such as the carbon cycle, nitrogen cycle, and water cycle, these cycles play a vital role in maintaining the balance of nutrients and energy within ecosystems. It is crucial that we continue to study and protect these cycles to ensure the health and sustainability of our planet for generations to come.