Phlebotomy is a critical aspect of healthcare that involves drawing blood for various tests and procedures. One essential concept in phlebotomy is the order of draw, which refers to the sequence in which blood samples are collected from patients. Following the correct order of draw is crucial to ensure accurate test results and prevent sample contamination.
Proper training and knowledge of the phlebotomy order of draw are essential for healthcare professionals to provide quality care to patients. By adhering to this protocol, phlebotomists can minimize the risk of errors and ensure that blood samples are collected efficiently and safely.
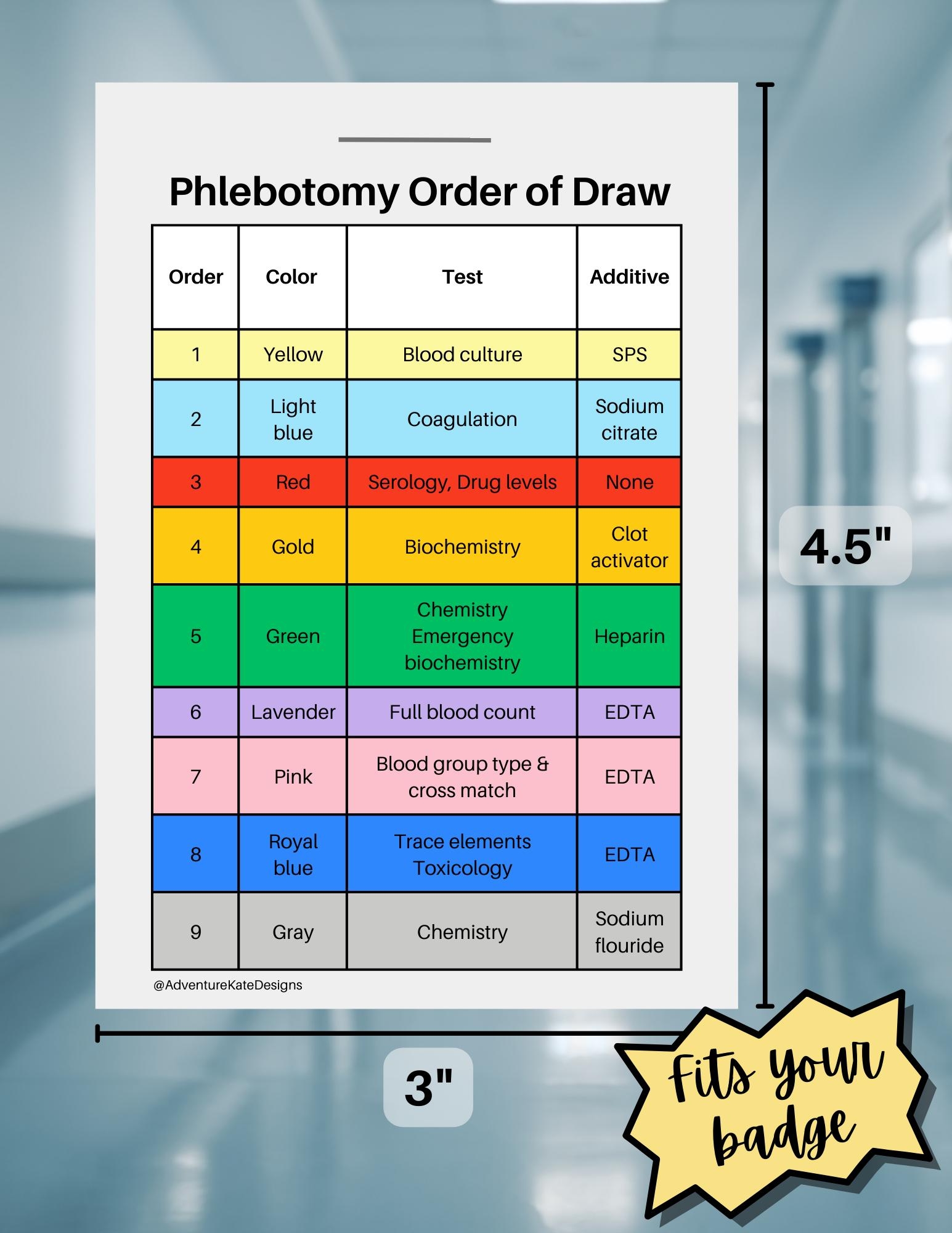
Phlebotomy Order of Draw
The phlebotomy order of draw is a standardized sequence that healthcare professionals follow when collecting blood samples for testing. The order of draw helps prevent cross-contamination between samples and ensures that test results are accurate. The following is the typical order of draw:
1. Blood cultures – These are typically collected first to prevent contamination from other samples.
2. Light blue top tubes (containing citrate) – Used for coagulation studies.
3. Red top tubes (no additive) – Used for chemistry tests.
4. Gold or tiger top tubes (containing gel separator) – Used for various chemistry tests.
5. Green top tubes (containing heparin) – Used for plasma determinations.
Following this order of draw helps ensure that each blood sample is collected in a clean, organized manner, reducing the risk of errors and contamination.
Phlebotomy order of draw is a critical concept that all healthcare professionals should understand and follow. By adhering to this protocol, phlebotomists can ensure the accuracy and reliability of blood test results, ultimately leading to better patient care and outcomes.
In conclusion, the phlebotomy order of draw is an essential component of the blood collection process in healthcare. By following the correct sequence, healthcare professionals can ensure the accuracy and reliability of blood test results, ultimately improving patient care and outcomes.